The industrial air-conditioning systems – ventilation technology
Air handling units are devices for the mechanical ventilation of rooms. Their primary function is to ensure the treatment and exchange of air inside buildings. Treatment consists of filtering, heating, cooling, humidifying or dehumidifying the air supplied to the premises.
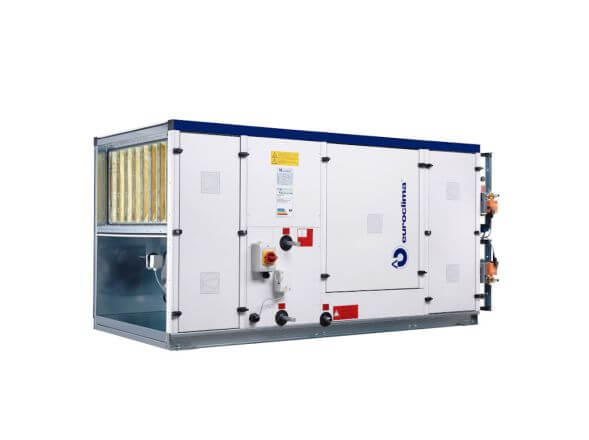
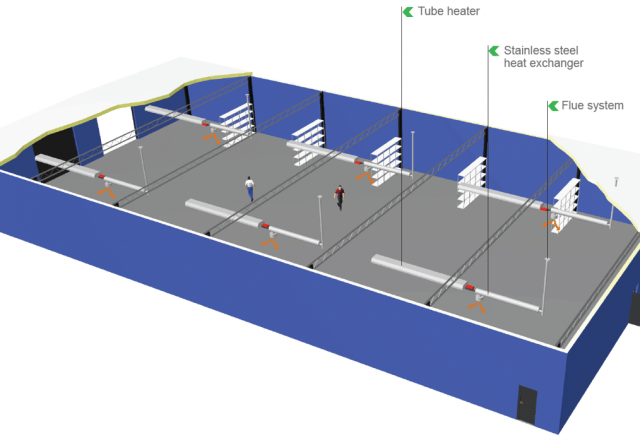
Air handling units (AHUs) consist of components for the respective air treatment function, which are commonly referred to as sections or modules. Depending on individual requirements, the combination of the relevant sections forms a ready-to-operate unit.
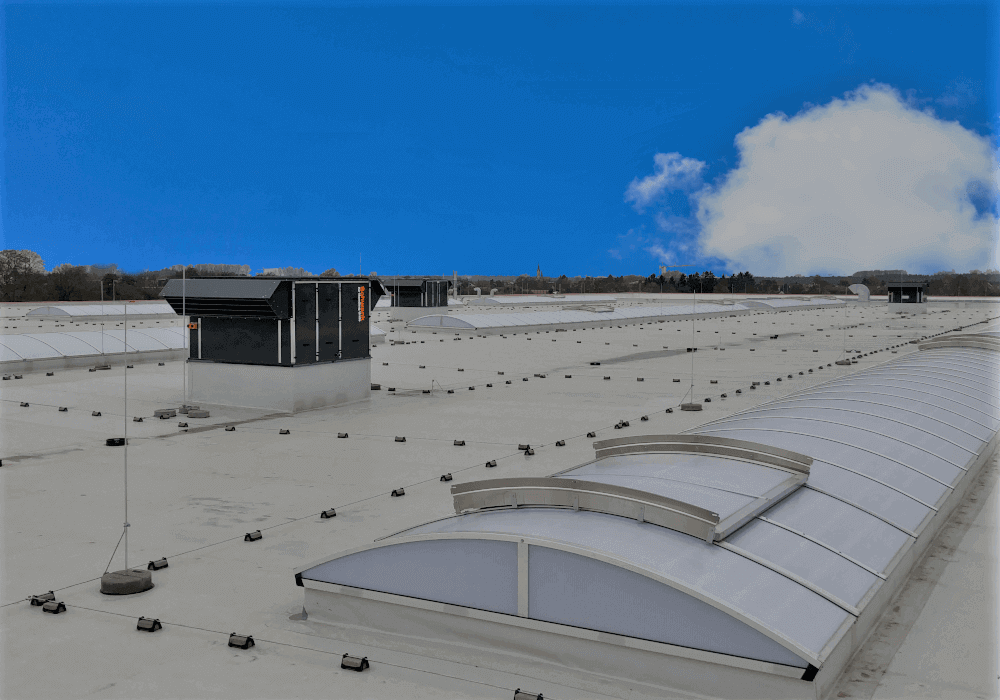
Air handling units can be installed outside or inside buildings. By means of ventilation ducts connected to the air handling unit, air is distributed to individual rooms.
Depending on their size, air handling units can exchange and process up to tens of thousands of m³ of air per hour.
What types of air treatment are carried out by air handling units?
In addition to managing proper ventilation and air exchange in buildings, air handling units also perform the following functions:
- Filtration with control of the quality of the air that is supplied to the premises. Thanks to the use of different degrees of filtration, the air supplied to the premises is fully purified.
- Control of air temperature, which is realised by heating or cooling the supply air to the premises.
- Monitoring and control of air humidity to ensure maximum occupant comfort in rooms or to meet the requirements of production processes.
What do air handling units consist of?
Air handling units consist of sections commonly referred to as modules. A section or module of an air handling unit is a sealed enclosure made of insulating panels, inside of which are installed the components that perform specific functions for the treatment of the air supplied to the premises. The following modules are used in air handling units:
- Filters (pre-filters, fine filters, HEPA, carbon filters)
- Heaters (water, glycol, electric, gas, freon)
- Fans (supply, exhaust)
- Coolers (water, glycol, freon, adiabatic)
- Heat recovery exchangers (heat recovery is realised by: recirculation, rotary heat recovery exchangers, crossflow – counterflow heat recovery exchangers, compressor heat pump module, glycol heat recovery exchangers)
- Acoustic silencers
- Humidifiers (isothermal steam humidifiers, adiabatic spray chambers, adiabatic spray beds)
- Disinfection sections with UV lamps
- Power supply module and control and measurement fittings
- Other components that provide the unit with specific functionality
The well thought-out unit design with the appropriate arrangement of the required modules and their correct dimensioning ultimately ensure the efficient and safe operation of an air handling unit.
Depending on the air purity requirements, the filters used may meet a higher or lower filtration class for particles, viruses, bacteria or odours and other air pollutants.
The fans draw in outside air, which, after treatment, is pumped through the ventilation duct system into the rooms of the building.
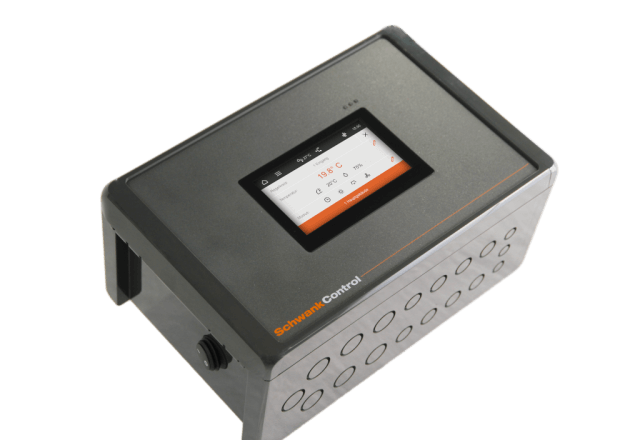
Control systems affect the efficiency of the installation and allow for efficient energy management. Remote management systems (BMS) offered by the manufacturer for air handling unit control systems are already standard. The quality of all control components ultimately affects the operation of the unit and the comfort of the occupants. Operation of the unit must be in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
What affects the quality of air handling units?
An important element that influences the durability of an air handling unit is the quality of the materials from which it is made: the grade of steel used and protective coatings, the type and quality of insulation materials, the temperature and UV resistance of plastics or the way in which all parts are protected from the effects of moisture or other aggressive agents – these aspects influence the quality and consequently the durability of air handling units. The quality of all components ultimately affects the operation of the unit and the comfort of the people inside.

Air handling unit: Euroclima
Air handling unit (AHU) efficiency
Air handling units marketed in the European Union have been subject to mandatory energy efficiency certification since 2016 under the European Ecodesign Regulation 1235/2014 implementing Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to Ecodesign requirements for ventilation equipment.
Through the use of various heat recovery methods, the air handling units reduce the consumption of thermal energy required for heating and cooling the air. In the process of heat recovery, the thermal energy accumulated in the exhaust air from the room is largely transferred (recovered) to the supply air, so that, the thermal energy required to heat or cool the air is reduced, thus reducing the total energy consumption of the unit over the whole year.
What types of air handling units are there?
Air handling units can be divided into types depending on their application: domestic recuperators, industrial recuperators, compact units, pool units, hygienic units, special units and freely configurable units.
Where can air handling units be installed?
Depending on the place of installation there are 2 types of air handling units:
- External – Rooftops (AHUs of this type are characterised by increased resistance to external conditions and are equipped with additional equipment, i.e. canopy, eaves, roof air intakes and outlets, additional panel insulation, control and instrumentation elements in UV-resistant design, dampers built inside the section).
- Internal (AHUs in the internal version are characterised by their standard design without the need for increased resistance to external conditions).
Performance and requirements for air handling units according to building characteristics.
Characteristics of building needs related to ventilation and air handling:
- Buildings and rooms with high concentrations of people and public facilities such as in hotels, function rooms (theatres, cinemas, auditoriums), restaurants, congress halls, airports, offices, schools, kindergartens, etc.
- Buildings and premises with high hygiene requirements such as laboratories, hospitals including operating theatres, sensitive production facilities, clean rooms, rooms with combustible and explosive atmospheres, etc.
Would you like individual advice on the right ventilation system?