What Requirements Do Warehouses Place on The Heating System?
In the logistical process, a considerable part of the warehousing costs is accounted for by the running costs of the building services. These include the maintenance of the doors, the maintenance of the sprinkler system, but also the warehpouse heating system. Although the majority of stored goods usually only require a minimum of heat, a warehouse heating system is indispensable, especially in the storage and retrieval process and in the logistical concept man to the goods. This is because the workplace ordinance stipulates that a heated workplace (for example, the order-picking area) with a room temperature of 17 °C must be provided for employees. On the one hand for health reasons, on the other for reasons of workplace satisfaction. Where people work, it must be warm and comfortable in winter.
However, the warehouse heating system also has other functions to fulfill. For example, outer packaging must be protected from moisture and the sprinkler systems must be kept frost-free and, if the goods are sensitive to oxidation such as bright steel, condensation must be kept free. The cold penetration mainly takes place in the loading and unloading areas. Even if the doors have approach buffers, there are large ventilation heat losses here during opening and closing times and during the loading and unloading process. In particular, the unit loads to be stored transport cold into the room, depending on their mass. In the worst case, a freshly brought-in item acts like a block of ice. In this case, the warmer room air would condense directly on the stored goods and thus form moisture.
The requirements for warehouse heating on the part of the operator are therefore:
- Low energy costs in order to keep storage costs low.
- Favorable acquisition costs.
- Fulfillment of the required comfort in order to comply with workplace guidelines.
- Functionality and reliability in order to keep the building’s facilities frost-free.
- Indoor air quality to protect stored goods from condensation and keep sprinklers frost-free.
Which Heating Systems Are Available for Warehouses?
Warm Air Heaters
- are either decentrally fired directly with gas or centrally supplied via a boiler.
- heat the entire room air.
- do not make individual space heating or zone heating possible.
- move air over large distances.
- generate noise through fans.
- are very energy-intensive in meeting comfort temperatures, but relatively inexpensive to purchase.
Underfloor Heating
- is centrally supplied via a boiler.
- is suitable for even heating of the entire building area.
- operates silently.
- makes the use of renewable energies possible.
- reacts only very slowly to room climate fluctuations.
- requires a lot of installation work and is expensive to purchase.
Hot Water Radiant Ceiling Panels
- are mounted under the building’s ceiling and centrally supplied with hot water.
- transmit the heat by means of infrared radiation.
- are also suitable for low building sections due to their low surface temperatures.
- make workplace and zone heating feasible.
- have system-related heat losses that occur in the heat transfer medium from the boiler to the radiant ceiling panel.
- make the use of regenerative energies possible.
- are a sluggish system for temperature adjustments.
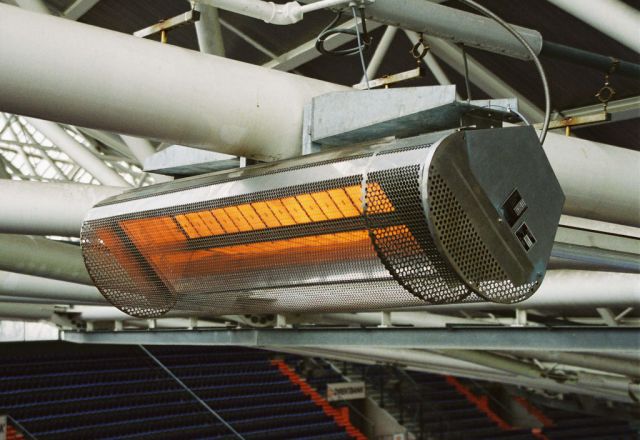
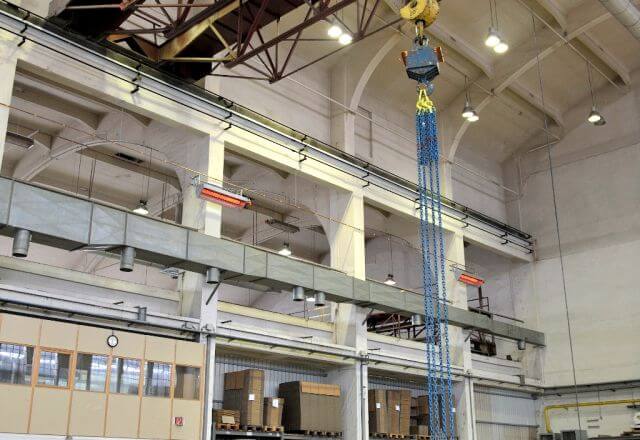
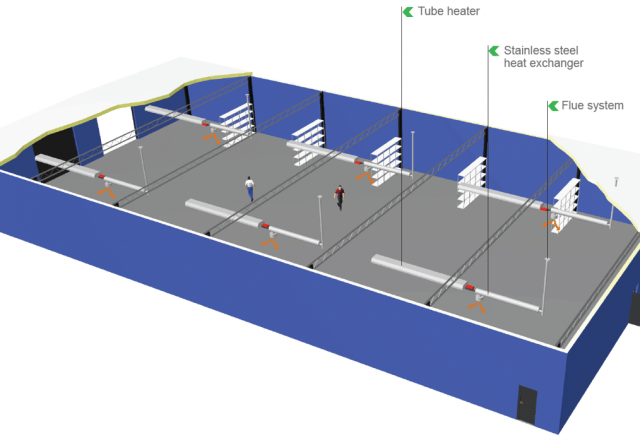
Tube Heaters
- generate comfortable infrared heat in the occupied area due to high surface temperatures.
- are also suitable for very high buildings.
- are operated decentrally directly with gas.
- are highly fail-safe.
- make workplace and zone heating very feasible.
- react quickly to temperature changes (reaction time).
- have a very energy-saving mode of operation as well as low purchase costs.
- are very flexible and direct in temperature control.
Which Warehouse Heating System Brings The Most Advantages?
Decentralised industrial heating systems are much more flexible than water-guided central heating systems. The advantages of underfloor heating or concrete core activation are offset by very high investment costs. In addition, special consideration must be given to the heated area in the event of changes of use.
Meanwhile, planners and builders of warehouses have discovered the advantages of infrared systems as warehouse heating. While radiant heaters primarily heat the floor, the walls, the stored goods and the employees, air-guided systems must constantly “heat up” against the escaping warm air, for example when the building’s doors are open or there are structural leaks. Tube heaters, on the other hand, bring the heat directly into the area where people are staying. The low energy consumption of the devices is also due to the fact that infrared heat is perceived as warmer by people. The room temperature can thus be reduced by about 3° C without any loss of comfort. On average, a reduction of 1° C saves about 6-7 % energy, so heating 3° C less saves 18-21 % energy.
Tube heaters are more convenient compared to hot water ceiling panels due to their flexibility in control and their higher surface temperatures (= better heat utilisation). In buildings with a high air exchange rate, it is not uncommon to save up to 50 % in energy costs compared to other warehouse heating systems.
But new buildings also benefit from efficiency. The reduction of CO₂ emissions has a direct effect depending on the energy savings. The possibility of supplementing tube heaters with heat recovery systems from the exhaust gas can facilitate the path to a CO₂-neutral warehouses.
Another decisive advantage for warehouse heating with infrared radiators is zone or workplace heating. If the heat is not primarily needed in the area of the shelves or transport routes, only the order-picking area can be heated with a few devices. Like a “heat island”, the temperatures for the employees can be regulated higher there, the other building areas remain unheated.
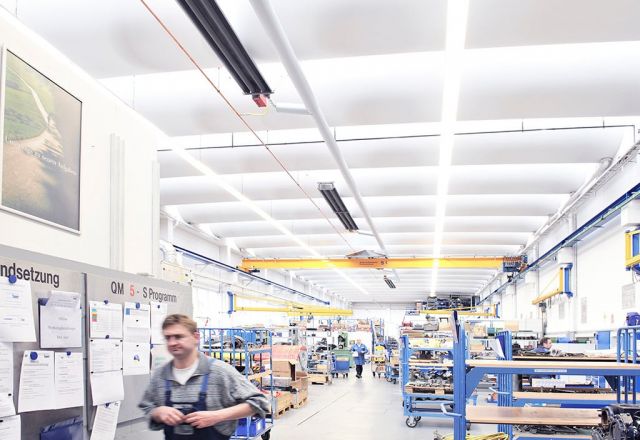
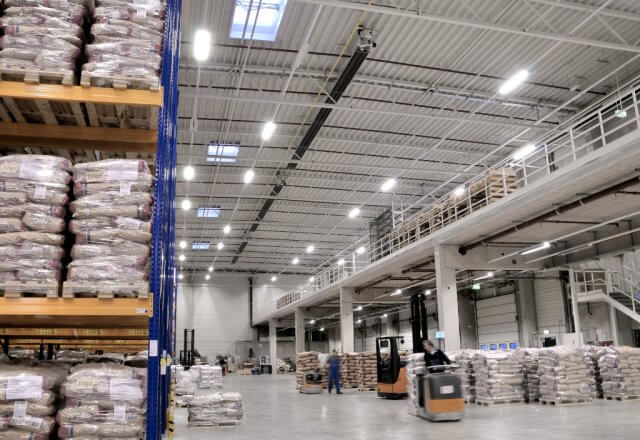
In warehouses, tube heaters are typically mounted under the ceiling in the door area. This does not restrict the storage area. Due to the high surface temperatures of the units, minimum distances to the stored goods must be observed.
Advantages of Tube Heaters as Warehouse Heating at A Glance
- particularly effective and energy-saving thanks to the high infrared radiation component
- low emissions due to low-NOx burner technology
- use of heat recovery systems possible
- future-proof, as manufacturers are already developing H2-ready, i.e. hydrogen-compatible, appliances
- highly economical, as no air needs to be heated and no expensive heat pads are created under the ceiling
- additional energy savings, as the room temperature can be regulated lower while maintaining the same comfort level
- fast reaction times to temperature fluctuations (through open doors)
- no dust or air turbulence
- heating of zones or individual workplaces is possible
- no freezing
- high reliability due to several burner units
Thanks to the considerable advantages of low initial costs and effectiveness, tube heaters are used in 70 % to 80 % of all warehouses, according to well-known general contractors and logistics investors.